What’s All the Hype about Hybrid Cloud with by Mark Dymond & Cynthia Unwin

Mark Dymond, Senior Partner at IBM, alongside his colleague Cynthia Unwin, Executive Architect presented the fifth seminar on What’s All the Hype about Hybrid Cloud? as part of the 2022-2023 IMI BIGDataAIHUB’s Seminar Series.
What is cloud computing?
Cloud computing, or “the cloud” is the delivery of on-demand computing resources—everything from applications to data centers – over the internet on a pay-for-use basis. Different services offerings include:
- Elastic resources: scale up or down quickly and easily meet changing demand
- Metered services: only pay for what you use
- Self-service: find all the IT resources you need, with self-service access

Most large organizations still have 50-60% of their technology on hardware, but typically anything new is built on the cloud. As companies shift to the cloud, they gain flexibility but lose control. In the shift to the cloud IT departments will typically start with low-risk applications. The pandemic sped-up cloud adoption, and digital transformation more broadly. However, over half of companies lack a clear strategy for digital transformation. Only a third of organizations feel that they are leveraging technology to the full extent that true digital transformation can provide. Security remains the largest barrier to more use of the cloud, as well as cost concerns. As such, hybrid cloud has become the dominant architecture globally.
Hybrid Cloud
Hybrid cloud is when cloud applications interact with on-premise applications or across different clouds. In other words, a hybrid cloud platform integrates applications that run across various clouds, moving data securely, and improving business workflows that span multiple clouds. A successful approach to hybrid cloud will allow you to build applications once and deploy them anywhere, manage applications once and host them anywhere, skill once and deploy them anywhere, and innovate anywhere with anyone’s technology.
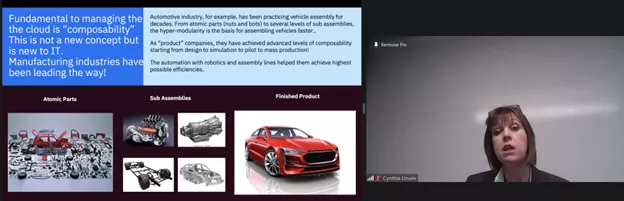
Composability and Multi-Cloud Models
Fundamental to managing the cloud is “composability.” The composability model reduces the need for specialized skills, democratizing the availability of technology, and resulting in scaled adoption. The multi-cloud model allows powerful cloud applications to be assembled from existing parts, quickly and easily, which drives speed, innovation, and scalability in a way that was not possible in previous models.
The Four V’s of Big Data
Organizations have access to vast amounts of contextual data. Where is all of this data coming from? Search engines, social media, mobile device subscriptions, and the Internet of Things devices provide a significant volume of data. Big data is defined by 4V’s: velocity, volume, variety, and veracity. Velocity is data being generated very fast, at a rate that never stops; and the speed at which data is transformed into insight. Volume is understood as the amount of data generated compared to traditional data sources. Variety refers to the different data sources from machines, people, and processes from both inside and outside organizations. Finally, veracity means the trustworthiness, quality, and origin of data.
Keys to Successful Big Data and Cloud Initiatives
- Ensure alignment to business value
- Be open to serendipitous insights
- Focus on automation, instrumentation, and tooling
- Be incremental-value driven
- Develop a common architectural framework
- Have intentional program setup, funding, ROI, KPIs, and measures
The high-level themes include having a comprehensive strategy that works iteratively. There must be top-level buy-in and support. Focus on driving incremental value through the integration of new data sources as they become available and new capabilities are required. Finally, adopt new ways of working to move quickly, fail fast, and reduce time-to-market cycles.